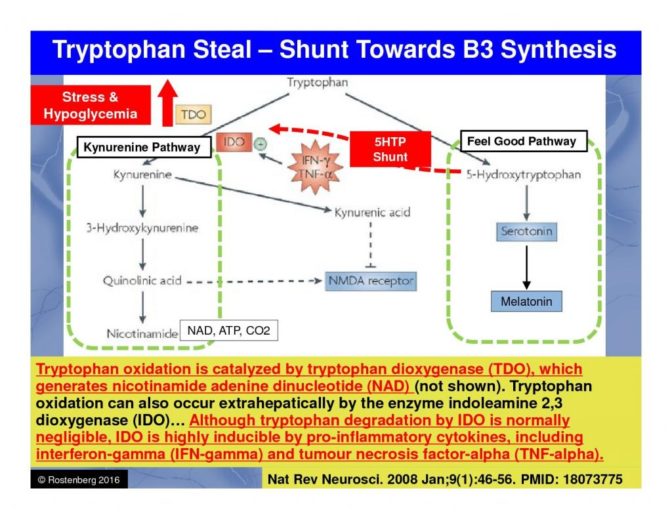
The increase in depression is most correlated with the increase in inflammatory autoimmune diseases and with significant changes in the western diet.
The US suicide rate has increased by 40% over the last 20 years.
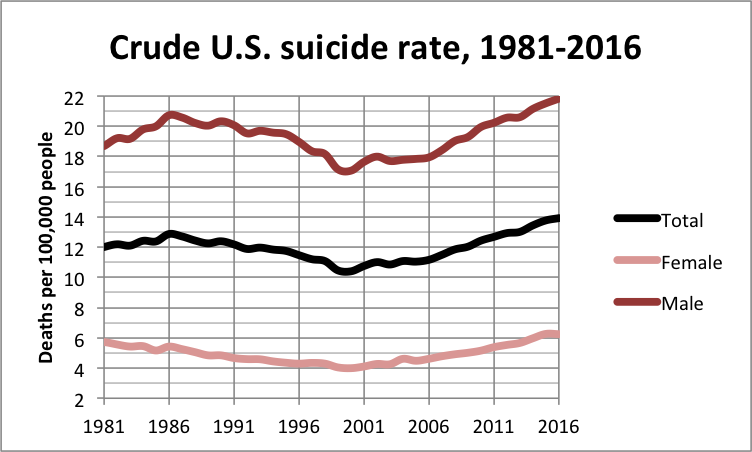
The increase in suicides that appeared around the year 2000 correlates highly with changes in the American diet starting around the year 2000.
One such change is the increase in vegetable oil consumption. This vegetable oil is often used in fried foods and contains many pro-inflammatory trans-fats.

The rise in suicides also correlates with a 10% decrease in vegetable intake. Vegetables themselves are generally anti-inflammatory.
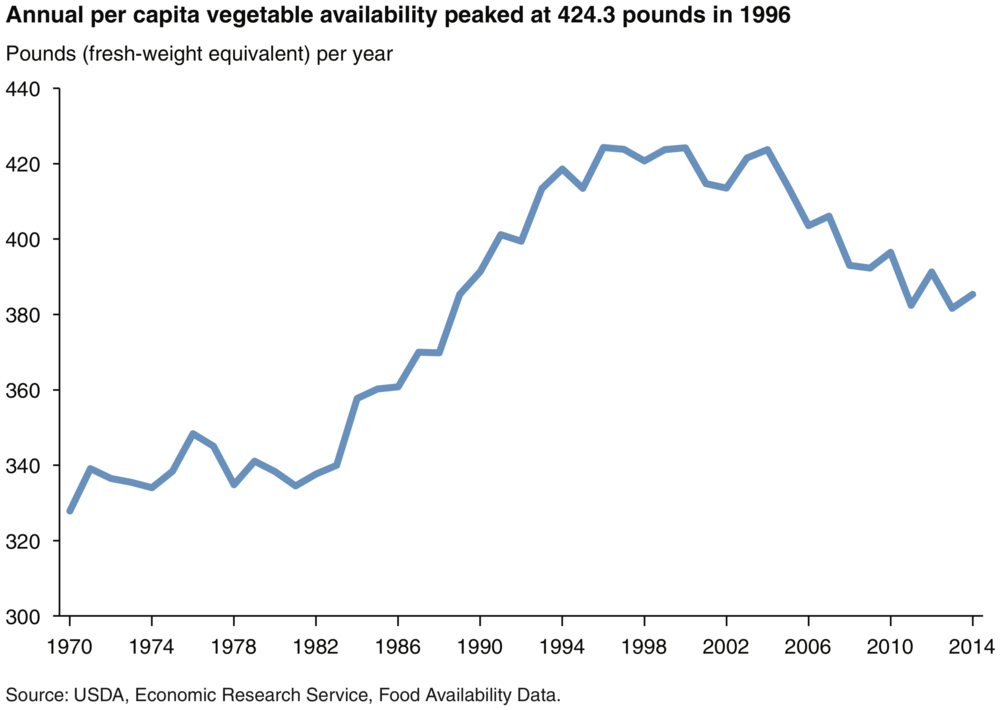
The rise in suicides also correlates with a 25% decrease in fruit intake. Fruit is also typically anti-inflammatory.

The prevalence of autoimmune disorders has been increasing for many decades.

If an individual has an autoimmune disease they are much more likely to also have depression and vice versa.

Depression has all of the hallmarks of sickness behavior triggered by the immune system when people are sick by inhibiting the production of serotonin and melatonin.

As shown above, our new diet is highly inflammatory so it’s triggering this sickness behavior all the time for many people.